In the realm of waste management and resource recovery, tyre pyrolysis plants have emerged as pivotal technologies. They convert end-of-life tyres into valuable by-products such as pyrolysis oil, carbon black, and syngas. Two main types of tyre pyrolysis plants exist: continuous and batch. Each has distinct operational principles, advantages, and drawbacks. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed investment and operational decisions.

Operational Principles
Continuous Tyre Pyrolysis Plant
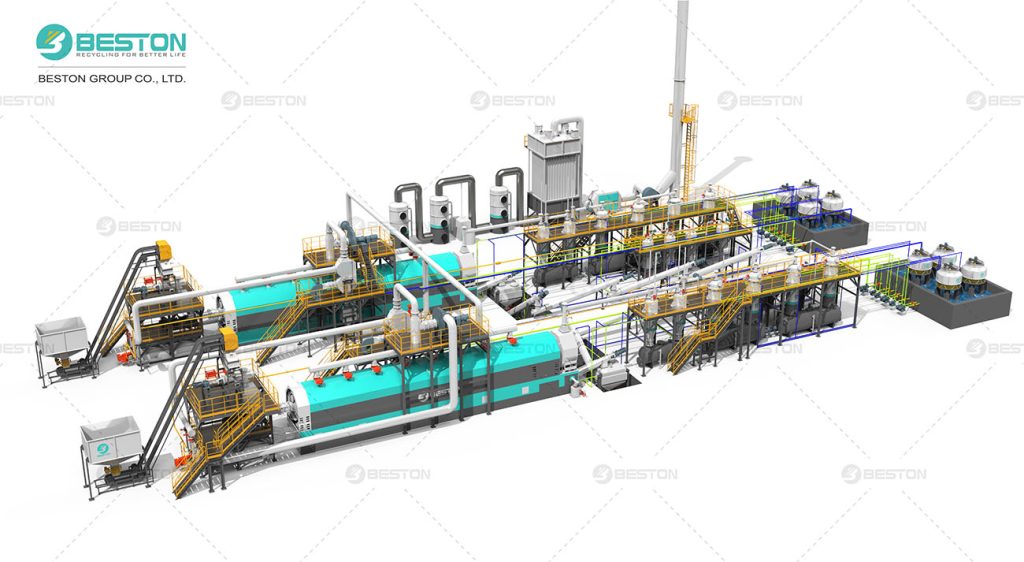
A continuous tyre pyrolysis plant operates without interruption. It processes tyres continuously, feeding raw materials at one end and discharging by-products at the other. This method is akin to an assembly line, ensuring a steady flow of materials and products.
Batch Tyre Pyrolysis Plant
In contrast, a batch tyre pyrolysis plant processes tyres in discrete batches. Each batch is loaded into the reactor, processed, and then the reactor is emptied before the next batch is introduced. This method involves periodic halts for loading and unloading, creating a cyclic operational pattern.
Efficiency and Throughput
Continuous Plant Efficiency
Continuous plants typically boast higher efficiency and throughput. The uninterrupted processing minimizes downtime and maximizes the volume of tyres processed within a given timeframe. This high efficiency is advantageous for large-scale operations where processing speed and volume are paramount.
Batch Plant Efficiency
The batch pyrolysis plant, while less efficient in terms of throughput, offer greater flexibility. They can easily adjust to varying quantities and types of feedstock. This adaptability is beneficial for smaller operations or those with fluctuating supply levels.
Energy Consumption
Energy Use in Continuous Plant
Continuous plants tend to consume more energy upfront to maintain the steady-state conditions required for continuous operation. However, once operational, they achieve better energy efficiency due to the constant thermal environment and reduced start-stop energy losses.
Energy Use in Batch Plant
Batch plants, on the other hand, experience significant energy fluctuations. The need to repeatedly heat up and cool down the reactor for each batch results in higher overall energy consumption compared to continuous plants. This cyclic energy demand can lead to increased operational costs.
Product Quality and Consistency
Product Quality in Continuous Plants
The consistent operating conditions of continuous plants often result in uniform product quality. The steady feed rate and controlled processing environment ensure that pyrolysis oil, carbon black, and syngas are produced with consistent properties, making them more predictable and easier to market.
Product Quality in Batch Plants
Batch plants may produce products with varying qualities due to the intermittent nature of the process. Each batch may encounter slightly different conditions, leading to variability in the chemical composition and properties of the by-products. This variability can be a challenge for end-users requiring consistent product specifications.
Maintenance and Operational Complexity
Maintenance in Continuous Plants
Continuous plants generally require more sophisticated maintenance protocols. The complexity of the system, with its myriad of conveyors, feeders, and continuous reactors, necessitates advanced maintenance schedules to prevent unexpected downtimes.
Maintenance in Batch Plants
Batch plants are relatively simpler to maintain. The discrete nature of their operation allows for easier access to the reactor and associated components. Maintenance can be performed between batches, reducing the impact on overall productivity.
Capital and Operational Costs
Costs of Continuous Plants
The initial capital investment for continuous plants is usually higher due to the complexity and scale of the equipment. However, the operational costs can be lower over time due to higher efficiency and lower energy consumption per unit of processed tyre.
Costs of Batch Plants
Batch plants often have lower upfront pyrolysis plant cost, making them more accessible for smaller enterprises or those with limited capital. The operational costs, however, can be higher due to increased energy consumption and potential downtime for maintenance and loading/unloading cycles.

Environmental Impact
Environmental Considerations for Continuous Plants
Continuous plants generally have a lower environmental footprint per unit of processed tyre. The consistent processing conditions lead to more complete pyrolysis reactions, reducing the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants.
Environmental Considerations for Batch Plants
Batch plants may have a higher environmental impact due to the variability in processing conditions and the potential for incomplete pyrolysis reactions. Proper management and mitigation strategies are essential to minimize emissions and environmental harm.
Flexibility and Scalability
Flexibility of Continuous Plants
Continuous plants offer limited flexibility. Once set up for a specific feed rate and processing condition, they are less adaptable to changes in feedstock quantity and type. This rigidity can be a disadvantage in dynamic supply environments.
Flexibility of Batch Plants
Batch plants excel in flexibility. They can easily adjust processing conditions to accommodate different types and quantities of feedstock. This adaptability makes them suitable for operations with variable supply chains or experimental setups.
Conclusion
Choosing between a continuous and batch tyre pyrolysis plant depends on various factors including scale of operation, feedstock supply, budget, and desired product quality. Continuous plants offer high efficiency, consistent product quality, and lower environmental impact but come with higher initial costs and operational complexity. Batch plants, while less efficient, provide greater flexibility, lower upfront costs, and simpler maintenance. Each type has its unique advantages and is suitable for different operational contexts. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions in the tyre pyrolysis industry. Consult Beston Company for more information on pyrolysis plants.